
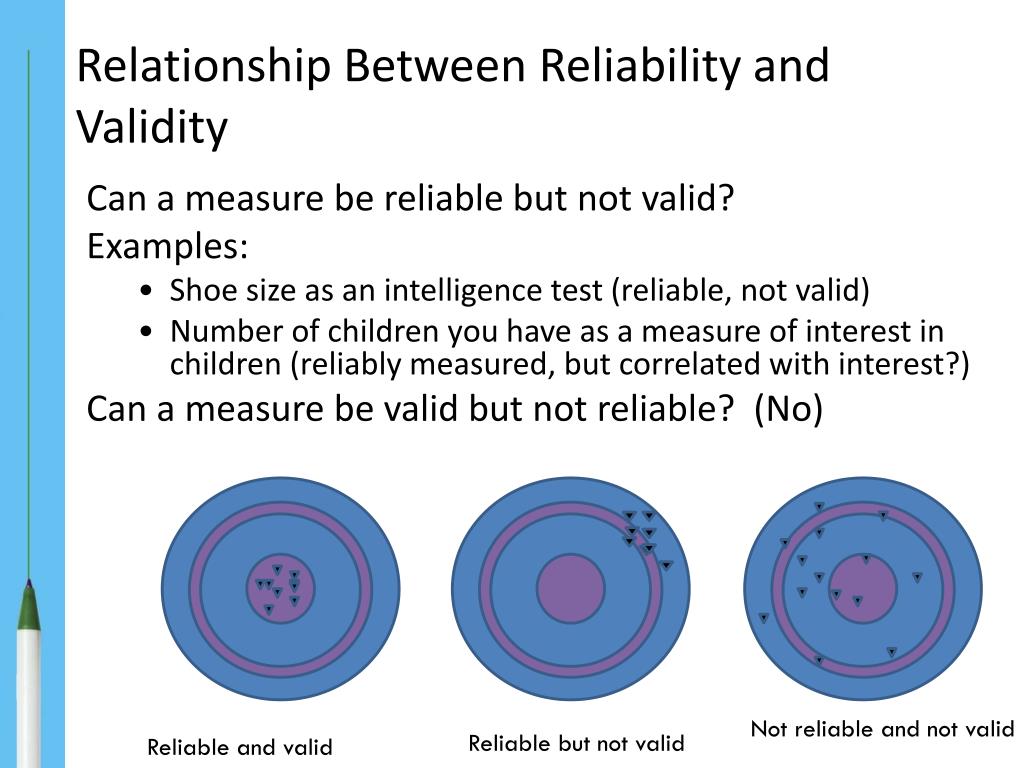
In essence, does it measure what it is supposed to measure? While there are several types of validity to pay attention to, the most important for our purposes is predictive validity. Validity refers to the accuracy of the assessment. Valid but not reliable means that the average scores align with the goals of the test, but individual scores are inconsistent.īoth reliable and valid means that the test will consistently measure what it is supposed to over a period of time – it’s consistently hitting the bullseye. Reliable but not valid means that you are consistently testing the same thing over and over again, but it’s not testing what you want to test. Validity and reliability can tell you two general things: 1) that the assessment is measuring what you want it to, and 2) that it will reliably assess the same thing each time - ensuring that the results you get aren’t a one-off.Īn easy way to think about this concept is with a bullseye metaphor: The very center of the bullseye is exactly what you want to assess. Any good tool should have concrete data demonstrating its validity and reliability. When deciding on the right assessment for your valuable talent, pay attention to the scientific rigor with which the instruments have been tested. Why bother using assessments that don’t predict performance, or that fail to resonate with your business leaders? Internal consistency reliability is a measure of reliability used to evaluate the degree to which different test items that probe the same construct produce similar results.Choosing the right assessment for selecting or developing employees can make or break the success of a talent initiative. Intra rater reliability is a measure in which the same assessment is completed by the same rater on two or more occasions.Ĭriterion validity is the measure where there is correlation with the standards and the assessment tool and yields a standard outcome. Parallel forms reliability is a measure of reliability obtained by administering different versions of an assessment tool (both versions must contain items that probe the same construct, skill, knowledge base, etc.) to the same group of individuals.Ĭontent validity is qualitative measure where the actual content matches the measurement which is a logical method of measurement. It includes constructs like concepts, ideas, theories, etc. Test-retest reliability is a measure of reliability obtained by administering the same test twice over a period of time to a group of individuals.Ĭonstruct validity seeks the implications between a theoretical concept and a specific measuring device. If the results cannot be replicated, the test is of little useĮxamples of different types of validity are:Įxamples of different types of reliability are:įace validity is when the tool appears to be measuring what it is supposed to measure with the content of test matching instructional objectives. If the results are not valid, the test is of no use at all Thus, usefulness of a test/experiments are negligible. When reliability/repeatability is poor, validity may also be poor.

There can be reliability without validity.Įven if validity of an instrument is poor (for certain test), it can have high reliability (for other tests) There cannot be validity without reliability Reliability is comparatively easier and yields faster results. Validity has more analysis and is harder to achieve. Influencing factors for reliability are: test length, test score variability, heterogenicity, etc. Influencing factors for validity are: process, purpose, theory matters, logical implications, etc. Reliability mainly focuses on maintaining consistent result Reliability looks at repeatability/consistency It relates to the extent to which an experiment, test or any procedure gives the same result on repeated trials.Ĭan relate to question of ‘Does it measure what it is supposed to measure’?Ĭan relate to question, ‘How representative is the measurement’?Īnswers, ‘Is it the right instrument/test for what I need to measure?’Īnswers, ‘Can the results obtained be replicated if the test is repeated?’ It relates to the correct applicability of the instrument/test/procedure in a needed situation It refers to the reproducibility of the results when repeated measurements are done

It refers to the ability of the instrument/test to measure what it is supposed to measure Reliability refers to the degree to which assessment tool produces consistent results, when repeated measurements are made. Validity implies the extent to which the research instrument measures, what it is intended to measure. Here you have all the major differences between Validity and Reliability and what it actually means: VALIDITY


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
